BAOJI ENERGY TITANIUM CO.,LTD.
Add:No.68 baoti road,hi-tech
zone,baoji,shaanxi,China.721013.
Email:emily@energytitanium.com
Tel: +86-917-3437683
Fax:+86-917-3437683
TECHNICAL INFORMATION OF TITANIUM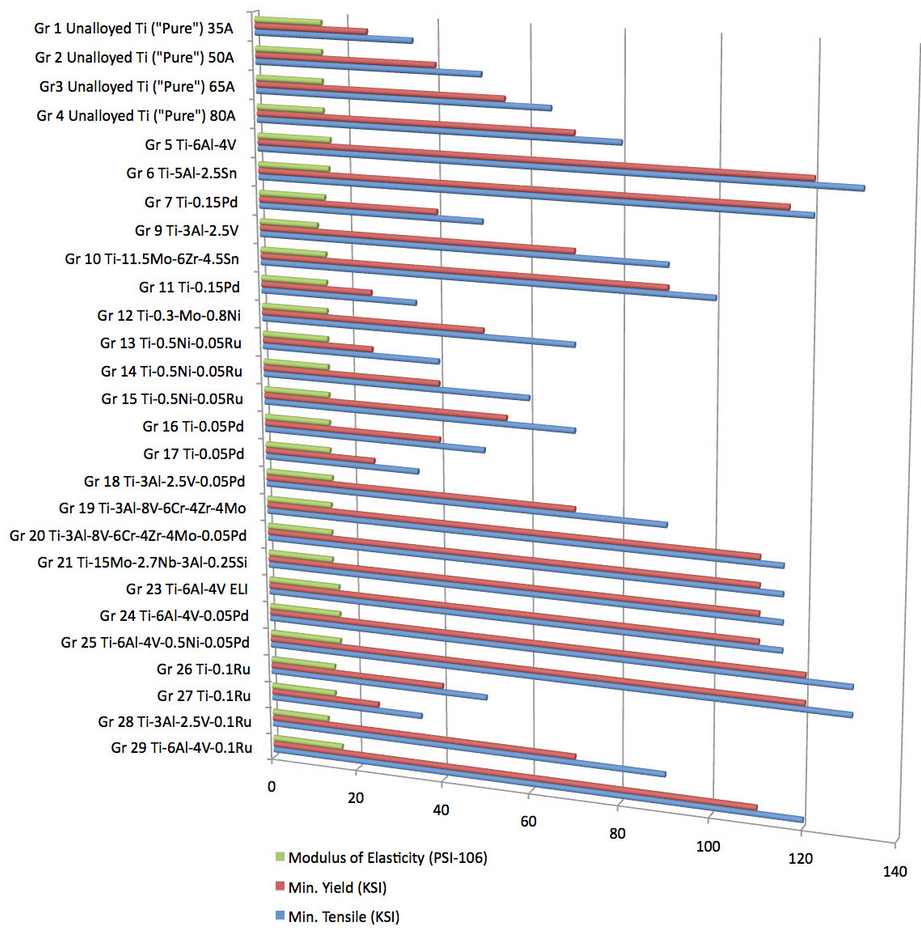
Most of the grades are of alloyed type with various additions of for example aluminum, vanadium, nickel, ruthenium, molybdenum, chromium or zirconium for the purpose of improving and/or combining various mechanical characteristics, heat resistance, conductivity, microstructure, creep, ductility, corrosion resistance etc. etc.
The mechanical properties of commercially pure titanium are in fact controlled by "alloying" to various levels of oxygen and nitrogen to obtain strength levels varying between approximately 290 and 550 MPa. For higher strength levels alloying elements, e.g. Al and V have to be added. Ti3Al2,5 V has a tensile strength of minimum 620MPa in annealed condition and minimum 860 MPa in the as cold worked and stress relieved condition. The CP-titanium grades are nominally all alpha in structure, whereas many of the titanium alloys have a two phase alpha + beta structure. There are also titanium alloys with high alloying additions having an entire beta phase structure. While alpha alloys cannot be heat treated to increase strength, the addition of 2,5% copper would result in a material which responds to solution treatment and ageing in a similar way to aluminum-copper.
Grade 1 is slightly purer than Grade 2 (at approximately 99.8%), and therefore more formable. It is used as the surface protective (titanium) layer in Explosively Clad (bonded) plate or parts, as well as for the complex shaped plates in Plate & Frame heat exchangers, due to its ability to be deep drawn.
Grade 2 is the most widely used of the CP (Commercially Pure) Grades. Products include Tube (welded & seamless), Pipe, Plate, Sheet/Strip, Fasteners, Fittings, Pumps and Valve bodies. It is approximately 99.6% pure and is the primary material for marine applications.
Grade 5 is the most widely used titanium alloy. It has very high strength but relatively low ductility. The main application of this alloy is in aircraft and spacecraft as well as in valves for industrial equipment. Offshore use is growing. The alloy is weldable and the precipitation can be hardened.
Grade 9 is a higher strength alloy, originally developed for increase of corrosion resistance for the Chemical Process Industry (CPI) for use in severe corrosive environments, designed to withstand crevice corrosion at low pH levels and at higher temperatures to 5000 °F (2600 °C). It has application in ship service as stack liners, providing corrosion resistance from the hot combustion gases and extending the (material replacement) life and port maintenance from every 6 months to several years.
Grade 23 is an Extra Low Interstitial (ELI) version of Grade 5. It is used where Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) is a concern, in applications where the 6Al – 4V alloy would normally be thought to be the material of choice, BUT where the application is under stress conditions. The lower interstitials (Fe, O2 and N2) give significant improvement to eliminating the SCC concerns.
| Previous:Titanium clad material Next:Nickel-based alloy series |





